核心架构
了解MCP如何连接客户端、服务器和LLM
model context protocol(MCP)建立在灵活、可扩展的架构之上,实现了LLM应用程序和集成之间的无缝通信。本文档涵盖了核心架构组件和概念。
概述
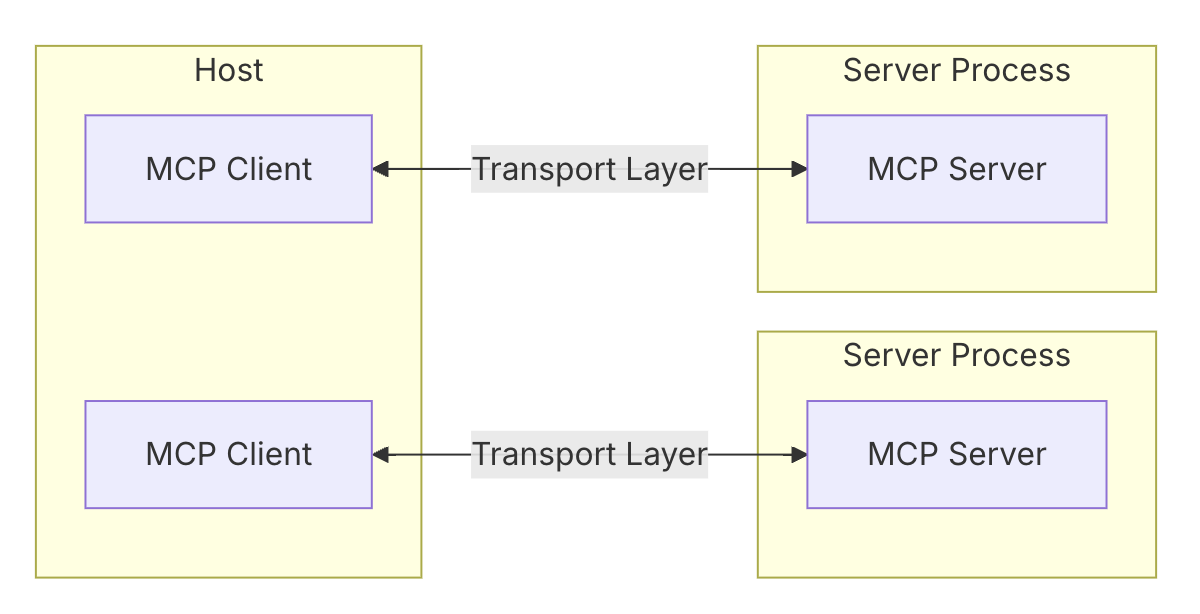
MCP遵循客户端-服务器架构,其中:
- 主机是启动连接的LLM应用程序(如Claude桌面版或IDE)
- 客户端在主机应用程序内与服务器保持1:1连接
- 服务器向客户端提供上下文、工具和提示
核心组件
协议层
协议层处理消息帧、请求/响应链接和高级通信模式。
typescript
class Protocol<Request, Notification, Result> {
// Handle incoming requests
setRequestHandler<T>(schema: T, handler: (request: T, extra: RequestHandlerExtra) => Promise<Result>): void
// Handle incoming notifications
setNotificationHandler<T>(schema: T, handler: (notification: T) => Promise<void>): void
// Send requests and await responses
request<T>(request: Request, schema: T, options?: RequestOptions): Promise<T>
// Send one-way notifications
notification(notification: Notification): Promise<void>
}python
class Session(BaseSession[RequestT, NotificationT, ResultT]):
async def send_request(
self,
request: RequestT,
result_type: type[Result]
) -> Result:
"""
Send request and wait for response. Raises McpError if response contains error.
"""
# Request handling implementation
async def send_notification(
self,
notification: NotificationT
) -> None:
"""Send one-way notification that doesn't expect response."""
# Notification handling implementation
async def _received_request(
self,
responder: RequestResponder[ReceiveRequestT, ResultT]
) -> None:
"""Handle incoming request from other side."""
# Request handling implementation
async def _received_notification(
self,
notification: ReceiveNotificationT
) -> None:
"""Handle incoming notification from other side."""
# Notification handling implementation关键类包括:
- Protocol
- Client
- Server
传输层
传输层处理客户端和服务器之间的实际通信。MCP支持多种传输机制:
Stdio传输
- 使用标准输入/输出进行通信
- 适用于本地进程
HTTP与SSE传输
- 使用服务器发送事件进行服务器到客户端的消息传输
- 使用HTTP POST进行客户端到服务器的消息传输 所有传输都使用JSON-RPC 2.0交换消息。有关model context protocol消息格式的详细信息,请参阅规范。
消息类型
MCP有以下几种主要消息类型:
- 请求期望从另一方得到响应:
typescript
interface Request {
method: string;
params?: { ... };
}- 结果是对请求的成功响应:
typescript
interface Result {
[key: string]: unknown;
}- 错误表示请求失败:
typescript
interface Error {
code: number;
message: string;
data?: unknown;
}- 通知是不期望响应的单向消息:
typescript
interface Notification {
method: string;
params?: { ... };
}连接生命周期
1. 初始化
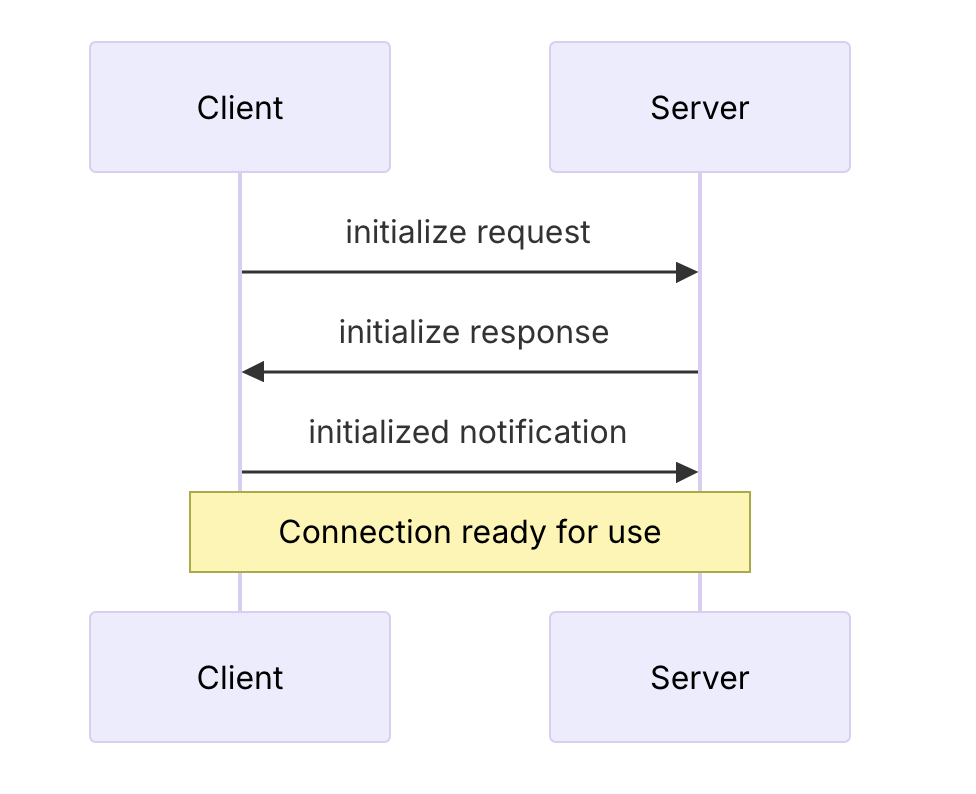
- 客户端发送带有协议版本和功能的初始化请求
- 服务器响应其协议版本和功能
- 客户端发送初始化通知作为确认
- 开始正常的消息交换
2. 消息交换
初始化后,支持以下模式:
- 请求-响应:客户端或服务器发送请求,另一方响应
- 通知:任何一方发送单向消息
3. 终止
任何一方都可以终止连接:
- 通过close()进行清理关闭
- 传输断开
- 错误条件
错误处理
MCP定义了这些标准错误代码:
typescript
enum ErrorCode {
// Standard JSON-RPC error codes
ParseError = -32700,
InvalidRequest = -32600,
MethodNotFound = -32601,
InvalidParams = -32602,
InternalError = -32603
}SDK和应用程序可以定义自己的错误代码(大于-32000)。
错误通过以下方式传播:
- 对请求的错误响应
- 传输上的错误事件
- 协议级错误处理程序
实现示例
以下是实现MCP服务器的基本示例:
typescript
import { Server } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/index.js";
import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js";
const server = new Server({
name: "example-server",
version: "1.0.0"
}, {
capabilities: {
resources: {}
}
});
// Handle requests
server.setRequestHandler(ListResourcesRequestSchema, async () => {
return {
resources: [
{
uri: "example://resource",
name: "Example Resource"
}
]
};
});
// Connect transport
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);python
import asyncio
import mcp.types as types
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
app = Server("example-server")
@app.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> list[types.Resource]:
return [
types.Resource(
uri="example://resource",
name="Example Resource"
)
]
async def main():
async with stdio_server() as streams:
await app.run(
streams[0],
streams[1],
app.create_initialization_options()
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main)最佳实践
传输选择
本地通信
- 对本地进程使用stdio传输
- 适用于同一机器上的高效通信
- 简单的进程管理
远程通信
- 在需要HTTP兼容性的场景中使用SSE
- 考虑包括身份验证和授权在内的安全影响
消息处理
请求处理
- 彻底验证输入
- 使用类型安全的架构
- 优雅地处理错误
- 实现超时机制
进度报告
- 对长时间操作使用进度令牌
- 增量报告进度
- 在已知时包含总进度
错误管理
- 使用适当的错误代码
- 包含有用的错误消息
- 在错误时清理资源
安全注意事项
传输安全
- 对远程连接使用TLS
- 验证连接来源
- 在需要时实现身份验证
消息验证
- 验证所有传入消息
- 清理输入
- 检查消息大小限制
- 验证JSON-RPC格式
资源保护
- 实现访问控制
- 验证资源路径
- 监控资源使用
- 限制请求速率
错误处理
- 不要泄露敏感信息
- 记录与安全相关的错误
- 实现正确的清理
- 处理DoS场景
调试和监控
日志记录
- 记录协议事件
- 跟踪消息流
- 监控性能
- 记录错误
诊断
- 实现健康检查
- 监控连接状态
- 跟踪资源使用
- 性能分析
测试
- 测试不同的传输方式
- 验证错误处理
- 检查边缘情况
- 负载测试服务器